Like any specialized hobby or discipline, the world of coin collecting has its own language. Understanding these terms will help you navigate coin dealer websites and build your collection with confidence.
A
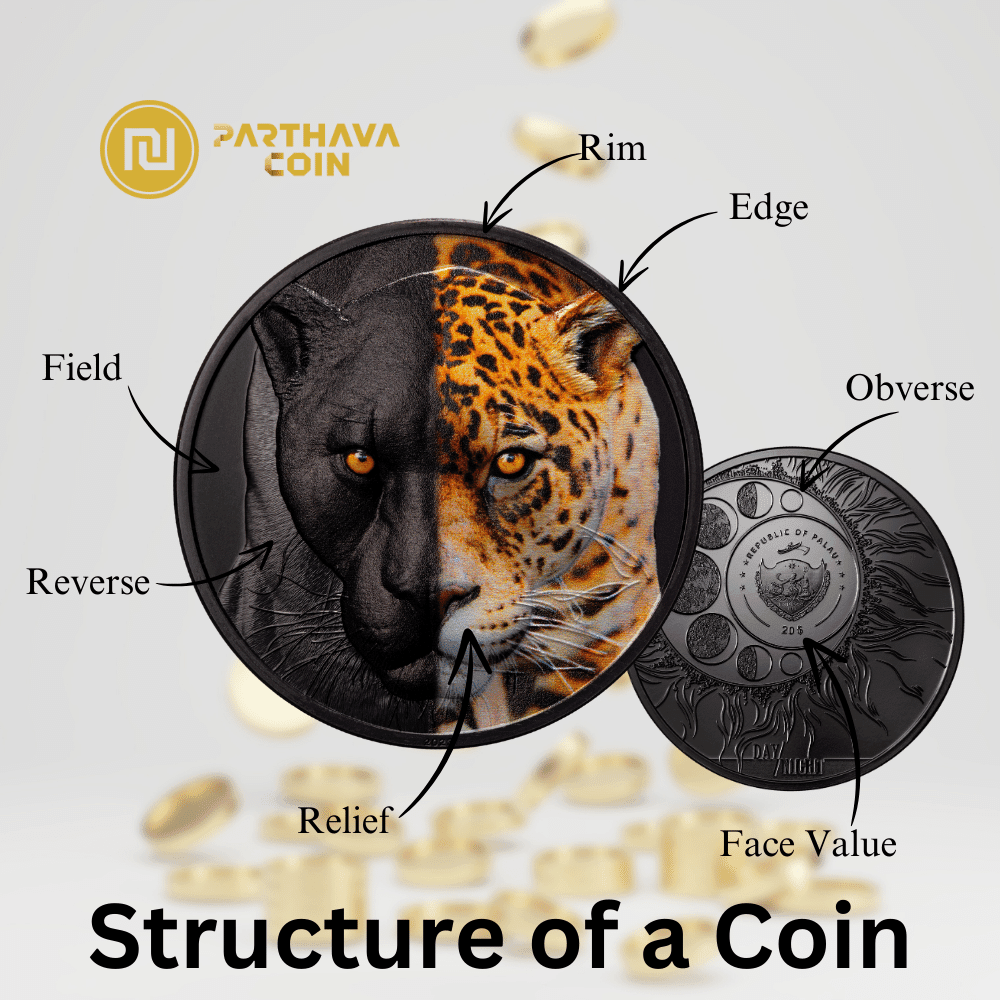
Anatomy of a Coin: The specific parts and features that make up a coin, including the obverse, reverse, rim, edge, field, and relief.
B
Brilliant Uncirculated Coins: A finish used on standard circulation coins, characterized by both the engraved design (relief) and background (field) being shiny.
Bullion: Bars, ingots, plates, wafers, or coins made from precious metals, usually gold or silver.
C
Circulation Coins: Coins that have been used in commerce and circulated among the general population.
Commemorative Coins: Coins minted to commemorate a particular event, person, place, institution, or issue. These are usually collector coins and are not circulated.
Coin Set: A collection of uncirculated or proof coins, released by a mint.
Composition: The material a coin is made from. Common compositions include 99.999% pure gold, 99.99% pure gold or silver, and 99.95% pure platinum.
E
Edge: The outer border of a coin, considered the "third side," which may be plain, serrated, or feature decorative elements.
Effigy: The image or likeness of a person, usually found on the obverse of a coin.
Encapsulated Coins: Coins that have been authenticated, graded, and preserved in a plastic case. Removing the coin from its capsule is not recommended.
Engraving: An artist's design that is adapted and transferred to a medium, ensuring the best relief for minting.
F
Face Value: The nominal value of a coin as indicated by the issuing authority.
Field: The flat background part of a coin where the relief is struck.
Finish: The appearance or surface texture of a coin's relief. Popular finishes include:
- Proof: A frosted relief over a brilliant field.
- Reverse Proof: Brilliant, mirror-like details on a frosted or matte field.
- Specimen: A brilliant image relief against a matte or lined background.
G
Grade: The condition of a coin, indicating the level of wear and any physical damages or changes in color or tone. Coins in mint condition have higher value.
I
Intrinsic Value: The actual value of a coin based on key factors such as purchase price, historical value, aesthetic features, mint year, scarcity, and collectability.
M
Matte Proof: A unique finish to the Royal Canadian Mint, similar to a standard proof but with a satin background, giving the coin an aged appearance while maintaining texture on the relief.
Mint: An industrial facility that manufactures coins (e.g., Royal Canadian Mint).
Minting: The process of manufacturing coins.
Mintage: The maximum number of coins that can be produced for a particular issue. Lower mintage coins are rarer and often more valuable.
N
Numismatics: The study or collection of coins or paper money.
Numismatist: A student or collector of coins or paper money.
P
Proof Coins: Coins minted using a high-quality finish. The field has a mirror-like finish, and the relief features various finishes to accentuate the design.
R
Relief: The raised, three-dimensional image found on a coin’s field.
Reverse: The "tails" side of a coin, usually depicting the chosen design.
Reverse Proof: Similar to a regular proof finish but reversed: the background is matte, and the engraved relief shines with a glass-like polish.
S
Specimen Coin: Coins with a finish that combines brilliant and frosted relief over a lined field, offering higher quality than uncirculated coins.
U
Uncirculated Coins: Coins that have never been circulated, often featuring a brilliant field over a brilliant relief.
By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you will enhance your understanding and appreciation of coin collecting, making your hobby more enjoyable and informed.


























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.